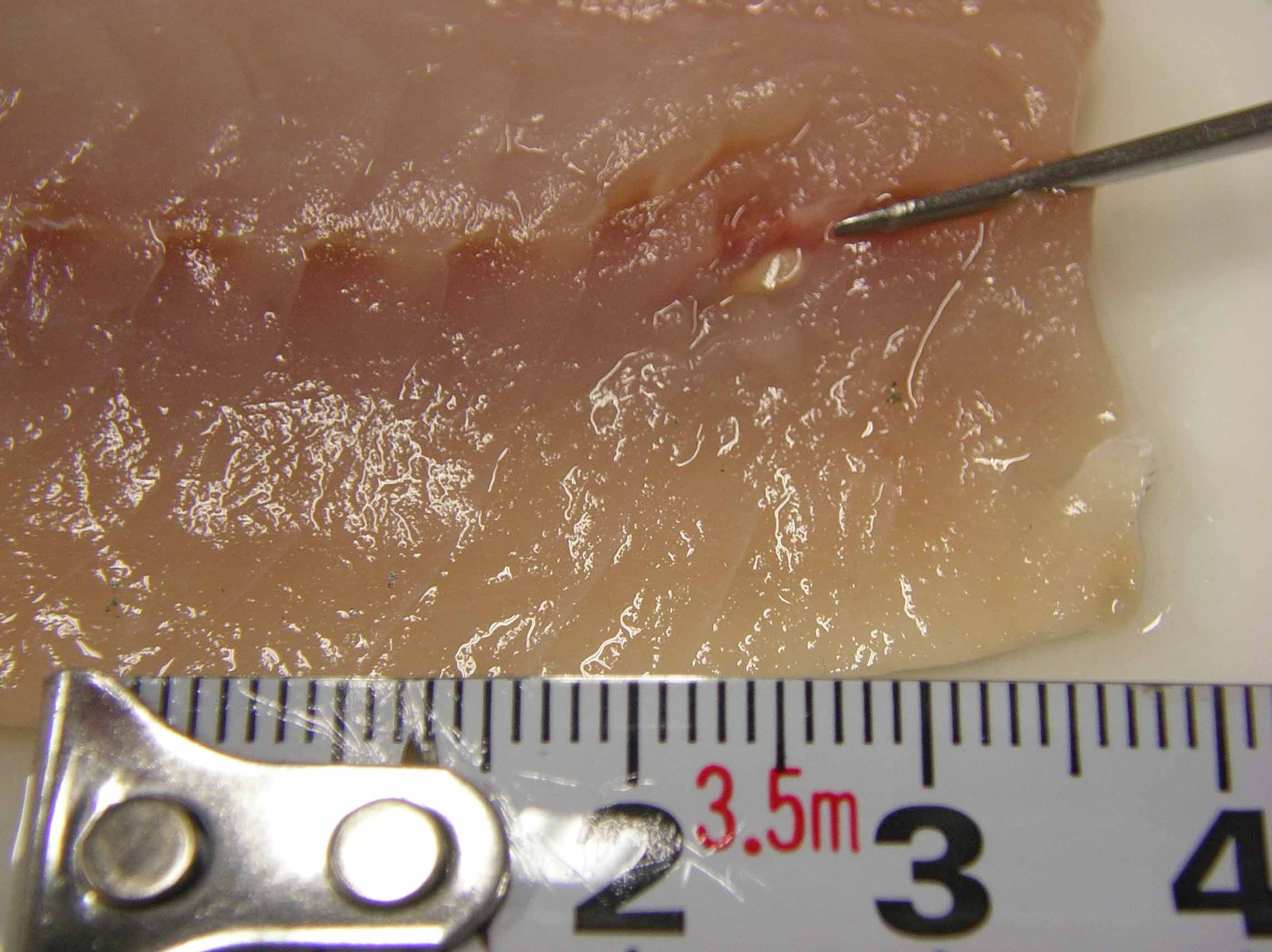

Fig. 1. Tentacularia in the muscle of Japanese jack mackerel.
Fig. 2. Tentacularia collected from the fish.
| Parasite | Tentacularia sp. |
|---|---|
| Taxonomy | Plathyhelminthes, Cestoda, Trypanorhyncha |
| Hosts | Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis), Japanese jack mackerel (Trachurus japonicus), Chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus) |
| Infection site | Trunk muscle |
| Clinical sign | No external signs are evident. Whitish bean-shaped parasites are observed in the trunk muscle (Fig. 1). |
| Parasitology | A larva of the parasite (ca. 5-10 mm) has 4 tentacles at the apical end of the head (scolex) and encased by host’s tissue (Fig. 2 and 3). The tentacle is armed with hooks (Fig. 4) and plays a role of an anchor. After the infected fish are ingested by shark (definitive host), the parasite develops into adult. |
| Pathology | No report |
| Health hazard | Since this parasite is not infectious to human, it is harmless in food hygiene. |
| Diagnosis | Larvae of Trypanorhyncha possess characteristic 4 tentacles at the apical end of the scolex. |
| Other information | This parasite is often found from spring to summer in the viscera and the ventral trunk muscle of skipjack tuna. |
Fig. 3. Four tentacles of Tentacularia
Fig. 4. Many hooks are seen on the tentacle.